|
Quick Guide
This part contains
some examples that help you get to use DevMic quickly. After passing through
these examples you will know how to create and compile a project with DevMic,
debug it with ProEmulator and getting some knowledge about writing software for
microcontrollers.
Example 1: Create a
simple project
1. Start DevMic by running (DevMic directory)\devmic.exe
2. Choose File > New > Project… to
create a new project
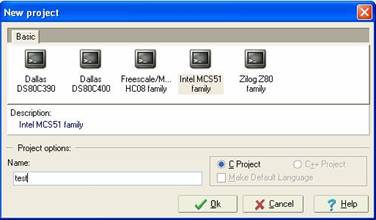
3. Choose Intel MCS51 family and type
the name of the Project. Click OK. Then choose directory where you want to save
the project.
4. Press F9 or choose menu Execute
à Compile to compile the project. If everything is OK, you will see the
Project1.ihx file in your project’s directory.
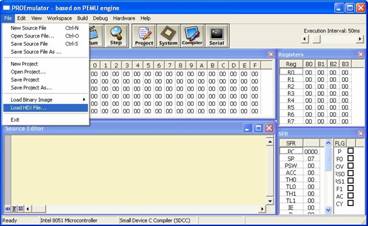
5. Now, we will show you how you can
debug your project with PROEmulator. Run PROEmulator in the (DevMic
directory)\micro\ProEmulator\ProEmulator.exe. Then choose menu File >
Load HEX File…
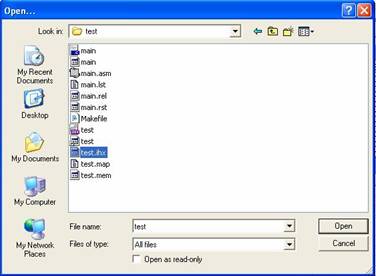
6. Choose file Project.ihx in your
project’s directory, then click Open (the binary format of Intel MCS51 is *.ihx)
7. Click icon Run to begin simulating
the operation of the Intel MCS51 family.
Click icon Stop to stop the simulating. Choose Data memory and click
Memory Walker, you will see
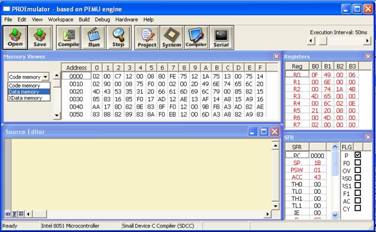
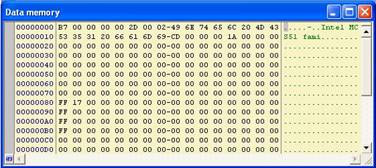
It means that everything’s coming
together. Now let’s move on to the next example.
Example 2: Test some
kinds of variable
1. We declare one integer variable
(located in Data Memory), one pointer of character (located in Xdata Memory)
and three bits
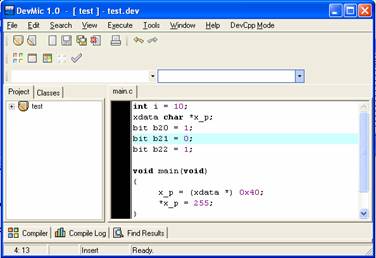
2. Compile it and run PROEmulator. After load
test.ihx, click Run icon and Stop icon, you will see
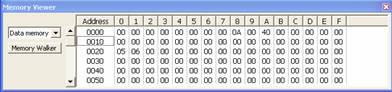
The value at 0x08 is 0A in Hexadecimal (10 in
Decimal). 3 bits in the program form a number in binary: 101. It equals to 05
in Hexa. The bit
addressable memory consists of 128 bits which are located from 0x20 to 0x2f in
data memory. Therefore you see the value 05 at 0x20. Turn to the Xdata Memory,
the value at 0x40 must be 0FF.
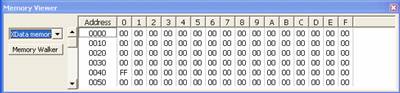
Now let’s move to more complex examples.
Example 3: Write
data to Xdata Memory
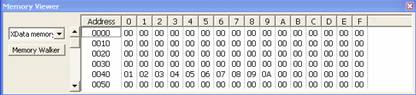
1. The objective of the program is write
data onto the Xdata Memory from 0x40 to 0x49. The value at 0x40 is 1, the value
at 0x41 is 2… the value at 0x49 is 10.
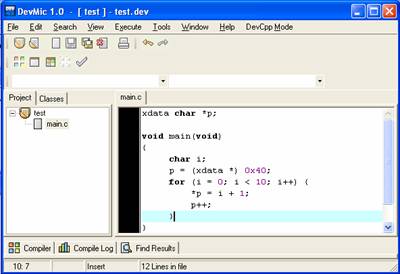
2. Compile it and use PROEmulator to check.
Example 4: Inline
assembly
1. The last example is rather interesting; it will
show you how to add Inline Assembly to your source. The
objective of the program is to assign 12 to DPTR register, move 0x0A to R0 and
assign the value 0x10 to the memory whose address lies in R0.
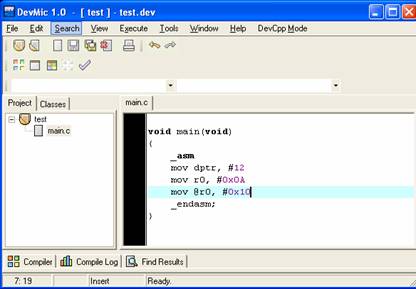
2. Compile it and use PROEmulator to check
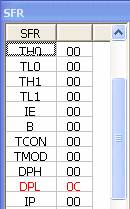 
You see in SFR, the value of DPH, DPL are 00, 0C
respectively. It means that the value of DPTR is 0x0C in Hexa or 12 in Decimal.
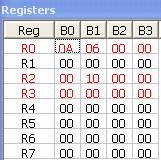
In Registes, R0 = 0x0A and at 0x0A the value is
0x10.
OK. Our examples have given you an overview about DevMic and
its features. Now it’s time for you to start building your own projects with
DevMic.
|